Acetaldehyde — toxicity, side effects, diseases and environmental impacts
11/08/2017 / By Michelle Simmons
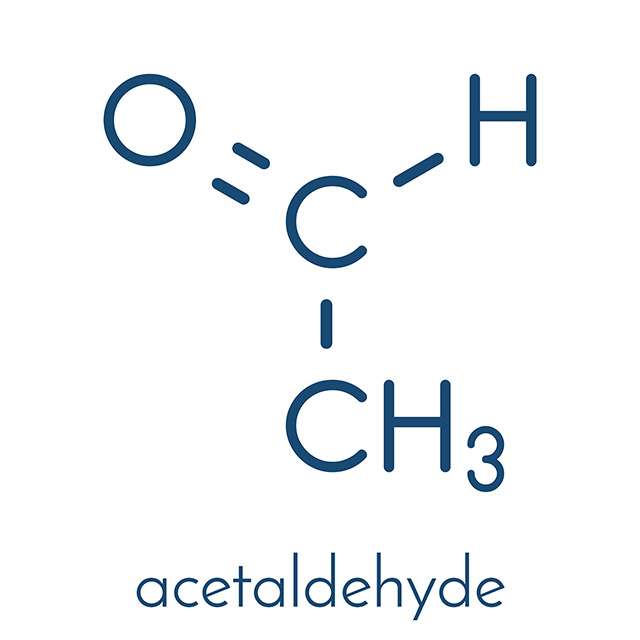
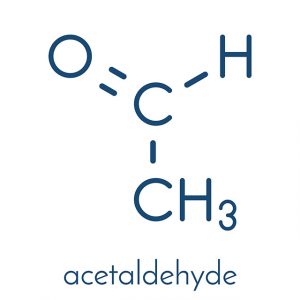
Acetaldehyde is a product of alcohol metabolism that is even more toxic than alcohol. It is produced when the liver breaks down alcohol through an enzyme called dehydrogenase. Glutathione in the liver quickly runs out when high amounts of alcohol enter the body. This results to the acetaldehyde accumulating in the body as the liver produces more glutathione, leaving the toxic substance in the body for long periods of time.
Acetaldehyde has a molecular formula of C2H4O.
List of known side effects
One of the side effects caused by acetaldehyde include vomiting. Acetaldehyde can also cause headaches. The toxic substance can also cause fatigue, irritation in the stomach, and a general sense of illness all over.
Body systems affected by acetaldehyde
There are a few body systems that are affected by acetaldehyde. The toxic substance affects the integumentary system as it may cause skin irritation and allergic skin reactions. Acetaldehyde also negatively affects the ocular system as it may cause serious eye damage and eye irritation when it comes in contact with the eyes. It also adversely affects the respiratory system when inhaled. It may cause drowsiness or dizziness. Furthermore, the toxic substance negatively affects the reproductive system as it may damage fertility or harm an unborn child.
Items that can contain acetaldehyde
Acetaldehyde is a naturally organic compound. This toxic substance can be found in yogurt, soy sauce, vinegar products, bread, ripe fruit, coffee, and brewers yeast. It is produced by plants or produced by the partial oxidation of alcohol by the liver enzyme alcohol dehydrogenase.
How to avoid acetaldehyde
According to an entry by BioHitHealthCare.com, acetaldehyde can be avoided by reducing or refraining from consuming alcohol. If you cannot stop drinking alcohol, drink at least those that contain mild alcohol instead of drinking hard liquor. Taking acetium capsules also lessens the amount of acetaldehyde in the stomach. Maintaining a high level of oral hygiene by brushing your teeth two times a day and before consuming alcohol, decreasing the microbial levels in the mouth, and having periodontal disease treated, if you have one, can all contribute towards the mitigation of acetaldehyde levels in the body.
Where to learn more
- Alcohol consumption is directly related to breast cancer: latest scientific facts
- So, we’re ALL aliens? New research suggests that DNA molecules were brought to Earth on meteorites
- Sugar Cravings and Candida
- The problem with alcohol in your mouthwash
- Drinking alcohol may raise the risk of prostate cancer
Summary
Acetaldehyde is a product of alcohol metabolism that is even more toxic than alcohol.
Acetaldehyde can cause vomiting, headaches, fatigue, irritation in the stomach, and a general sense of illness.
Acetaldehyde adversely affects the integumentary, ocular, respiratory, and reproductive systems.
Sources include:
Health.HowStuffWorks.com
PubChem.NCBI.NLM.NIH.gov
HappyHourVitamins.com
BioHitHealthCare.com
Tagged Under: acetaldehyde



















